Interventional Services

Safe

Local

Fast

Efficient

No Pain

Economic
Playlist
Our Services Include Include

Our Services Includes

Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms

Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is an enlarged area in the lower part of the aorta, the major blood vessel that supplies blood to the body. The aorta, about the thickness of a garden hose, runs from your heart through the center of your chest and abdomen. Because the aorta is the body’s main supplier of blood, a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm can cause life-threatening bleeding.
Benefits of Interventional Repair.
- No abdominal surgical incision.
- No sutures, or sutures only at the groins.
- Faster recovery, shorter time in the hospital.
- No general anesthesia in some cases.
- Less pain, and reduced complications.

Angiography or
Angiogram

Angiography or Angiogram
Interventional radiologists use imaging to diagnose, understand and visualize the full scope of the pathology and to map out the procedure tailored to the individual patient. Angiography is an X-ray exam of the arteries and veins to diagnose blockages and other blood vessel problems.
Reasons for Performing Angiography or Angiogram.
- aneurysms – an area of a blood vessel that bulges or balloons out.
- cerebral vascular disease, such as stroke or bleeding in the brain.
- blood vessel malformations.
- blockage or narrowing in a blood vessel.
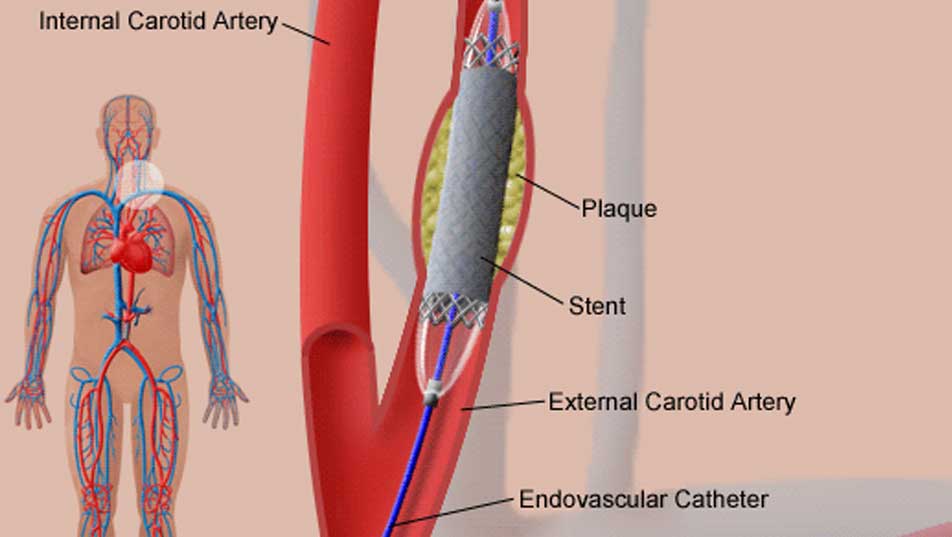
Angioplasty and stent placement

Angiography or Angiogram
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called the coronary arteries. A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that expands inside a coronary artery. A stent is often placed during or immediately after angioplasty. It helps prevent the artery from closing up again. A drug-eluting stent has medicine embedded in it that helps prevent the artery from closing in the long term.
Angioplasty may be used to treat:
- Blockage in a coronary artery during or after a heart attack.
- Blockage or narrowing of one or more coronary arteries that puts you at risk for a heart attack.
- Narrowings that reduce blood flow and cause persistent chest pain (angina) that medicines do not control.
In general, people who have angioplasty are able to walk around within 6 hours after the procedure. Complete recovery takes a week or less. You will be given information about how to care for yourself after angioplasty.

SIRT / Yttrium Microsphere

SIRT / Yttrium Microsphere
Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) is a treatment for liver cancers or tumors that delivers millions of tiny radioactive microspheres or beads called SIR-Spheres directly to the liver tumors. SIR-Spheres are approved for the treatment of liver tumors that cannot be removed by surgery. These may be tumors that start in the liver, or they may be tumors that have spread to the liver from another part of the body.
Benefits of SIRT:
- Greater survival benefit than just using chemotherapy alone.
- Reducing the sizes of tumors.
- Allowing some patients to have a liver transplant.
For most patients, treatment will result in increased survival time, but not a permanent cure.

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but may occur without any symptoms.Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition because blood clots in your veins can break loose, travel through your bloodstream and lodge in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism).
Deep vein thrombosis signs and symptoms can include:
- Swelling in the affected leg. Rarely, there may be swelling in both legs.
- Pain in your leg. The pain often starts in your calf and can feel like cramping or a soreness.
If you develop signs or symptoms of deep vein thrombosis, contact your doctor for guidance.

Pulmonary embolism

Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is when one or more pulmonary arteries in your lungs become blocked. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs or rarely other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT).Because pulmonary embolism almost always occurs in conjunction with deep vein thrombosis, some doctors refer to the two conditions together as venous thromboembolism (VTE).
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath. This symptom typically appears suddenly and always gets worse with exertion.
- Chest pain. You may feel like you’re having a heart attack. The pain may become worse when you breathe deeply (pleurisy), cough, eat, bend or stoop.
- Cough. The cough may produce bloody or blood-streaked sputum.
Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening, but prompt treatment can greatly reduce the risk of death. Taking measures to prevent blood clots in your legs also can help protect you against pulmonary embolism.

Gastrostomy feeding tube

Gastrostomy feeding tube
People with certain diseases or medical conditions sometimes require that tubes be placed into the body so that they can receive medications or nutrients directly into the blood stream or gastrointestinal system, or so blood can be drawn. Once, surgery was required to insert these tubes, but today these procedures can be done without surgery by an interventional radiologist.
Doctors often recommend CVACs for patients who regularly have:
- Chemotherapy treatments.
- Infusions of antibiotics or other medications.
- Nutritional supplements.
- Hemodialysis
Doctors often recommend placing a gastrostomy tube in the stomach for a variety of conditions in which a patient is unable to take sufficient food by mouth. In the procedure, the feeding tube is inserted through a small nick in the skin and into the stomach under X-ray guidance.

Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telanglectasia

Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telanglectasia
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, also known as HHT or Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, is an inherited disorder that affects blood vessels. In most cases, HHT isn’t life-threatening. Currently there’s no cure, but in many cases the symptoms can be effectively managed.This can lead to a variety of symptoms depending on where the blood vessel abnormality is located. In some areas of the body — especially the lungs, brain and liver — these blood vessel abnormalities can be serious because they may bleed, don’t allow for adequate oxygen levels in the blood, and can increase your risk of brain infections and stroke.
What ca we do:
- Lung: Interventional radiologists, can permanently treat lung AVMs using a minimally invasive procedure known as embolization.
- Brain: Embolization and stereotactic radiosurgery are treatment options that can be used separately or in combination.
Interventional radiologists treat malformations in the lung and brain using embolization.

Renal Hypertension

Renal Hypertension
Renal hypertension, also called renovascular hypertension, is elevated blood pressure caused by kidney disease. It can usually be controlled by blood pressure drugs. Some people with renal hypertension can be helped by angioplasty, stenting, or surgery on the blood vessels of the kidney. Renal hypertension is caused by a narrowing in the arteries that deliver blood to the kidney. One or both kidneys’ arteries may be narrowed. This is a condition called renal artery stenosis.
Symptoms of Renal Hypertension:
- Headache.
- Confusion.
- Blurry or double vision.
- Bloody (pink-colored) urine.
- Nosebleed.
Angioplasty, and most effectively Stenting are performed by our experts to treat such cases.

Female Infertility

Female Infertility
The most common cause of female infertility is a blockage of the fallopian tube through which eggs pass from the ovary to the uterus. Occasionally, these tubes become plugged or narrowed, preventing successful pregnancy. Interventional radiologists can diagnose and treat a blockage in the fallopian tubes with a nonsurgical procedure known as selective salpingography.
In the procedure, which does not require an incision:
- a catheter is placed into the uterus.
- A contrast agent, or dye, is injected through the catheter.
- and an X-ray image of the uterine cavity is obtained.
- When a blockage of the fallopian tube is identified, another catheter is threaded into the fallopian tube to open the blockage.
- When a blockage of the fallopian tube is identified, another catheter is threaded into the fallopian tube to open the blockage.
Some common causes of infertility in both women and men can now be treated without surgery by interventional radiologists. Often these treatments do not require hospitalization or general anesthesia. Patients usually may return to normal activity shortly after the procedure.

Male Infertility

Male Infertility
A varicocele is a varicose vein of the testicle and scrotum that may cause pain, testicular atrophy (shrinkage) or fertility problems. Veins contain one-way valves that work to allow blood to flow from the testicles and scrotum back to the heart. When these valves fail, the blood pools and enlarges the veins around the testicle in the scrotum to cause a varicocele. Varicocele embolization, a nonsurgical treatment performed by an interventional radiologist, is as effective as surgery with less risk, less pain and less recovery time.
In the procedure, which does not require an incision, an interventional radiologist:
- makes a tiny nick in the skin at the groin using local anesthesia.
- through which a thin catheter (much like a piece of spaghetti) is passed into the femoral vein directly to the testicular vein.
- by using coils, balloons, or particles, the interventional radiologist blocks the blood flow in the vein which reduces pressure on the varicocele.
- By embolizing the vein, blood flow is re-directed to other healthy pathways.
By embolizing the vein, blood flow is re-directed to other healthy pathways.

Liver Disease

Liver Disease
There are a number of problems in the liver that can be treated with nonsurgical, interventional radiology techniques.
- Portal Hypertension: portal hypertension is a condition in which the normal flow of blood through the liver is slowed or blocked by scarring or other damage. Patients with the condition are at risk of internal bleeding or other life-threatening complications. Interventional radiologists treat portal hypertension without surgery, using a procedure called TIPS (transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt). The doctor threads a catheter through a small incision in the skin near the neck and guides it to the blocked blood vessels in the liver. Under X-ray guidance, the doctor creates a tunnel in the liver through which the blocked blood can flow. The tunnel is held open by the insertion of a small metal cylinder, called a stent.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: In some patients, such as those with liver cancer or individuals who have had an injury to the liver, the bile ducts become blocked and bile cannot drain from the liver. The interventional radiologist places a catheter through the skin and into the bile ducts to drain the bile. A catheter may also be placed to drain bile in patients who have a hole in the bile ducts or as preparation for surgery on the bile ducts.
Our experts performed more than thousand alike procedure.

Needle biopsy

Needle biopsy
A needle biopsy is a procedure to obtain a sample of cells from your body for laboratory testing. Common needle biopsy procedures include fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy. Needle biopsy may be used to take tissue or fluid samples from muscles, bones and organs, such as the liver or lungs.
The sample from your needle biopsy may help your doctor determine what’s causing:
- A mass or lump. A needle biopsy may reveal whether a mass or lump is a cyst, an infection, a benign tumor or cancer.
- An infection. Analysis from a needle biopsy can help doctors determine what germs are causing an infection so that the most effective medications can be used.
- Inflammation. A needle biopsy sample may reveal what’s causing inflammation and what types of cells are involved.
- Inflammation. A needle biopsy sample may reveal what’s causing inflammation and what types of cells are involved.
Inflammation. A needle biopsy sample may reveal what’s causing inflammation and what types of cells are involved.

Osteoporosis Pain Treatment

Osteoporosis Pain Treatment
Osteoporosis is often called the “silent disease,” because most of the time, bone loss occurs without any symptoms at all. But when osteoporosis becomes severe, it can lead to fractures and a condition called kyphosis. Kyphosis is spinal compression, sometimes described as the “dowager’s hump.” Both fractures and kyphosis can be very painful. This pain is usually more severe than the typical “aches and pains” many people feel as they get older.
Vertebroplasty is an outpatient procedure using X-ray imaging and conscious sedation. The interventional radiologist:
- inserts a needle through a nick in the skin in the back, directing it under fluoroscopy (continuous, moving X-ray imaging) into the fractured vertebra.
- The physician then injects the medical-grade bone cement into the vertebra.
- The cement hardens within 15 minutes and stabilizes the fracture, like an internal cast.
Some patients experience immediate pain relief after vertebroplasty. Most report that their pain is gone or significantly better within 48 hours. Many people can resume their normal daily activities immediately.

Peripheral Artery Disease

Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (also called peripheral arterial disease) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to your limbs. When you develop peripheral artery disease (PAD), your extremities — usually your legs — don’t receive enough blood flow to keep up with demand. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (intermittent claudication).
Peripheral artery disease symptoms include:
- Painful cramping in your hip, thigh or calf muscles after activity.
- Leg numbness or weakness.
- Coldness in your lower leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side.
- Sores on your toes, feet or legs that won’t heal.
- A change in the color of your legs.
- Hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs.
Hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs.

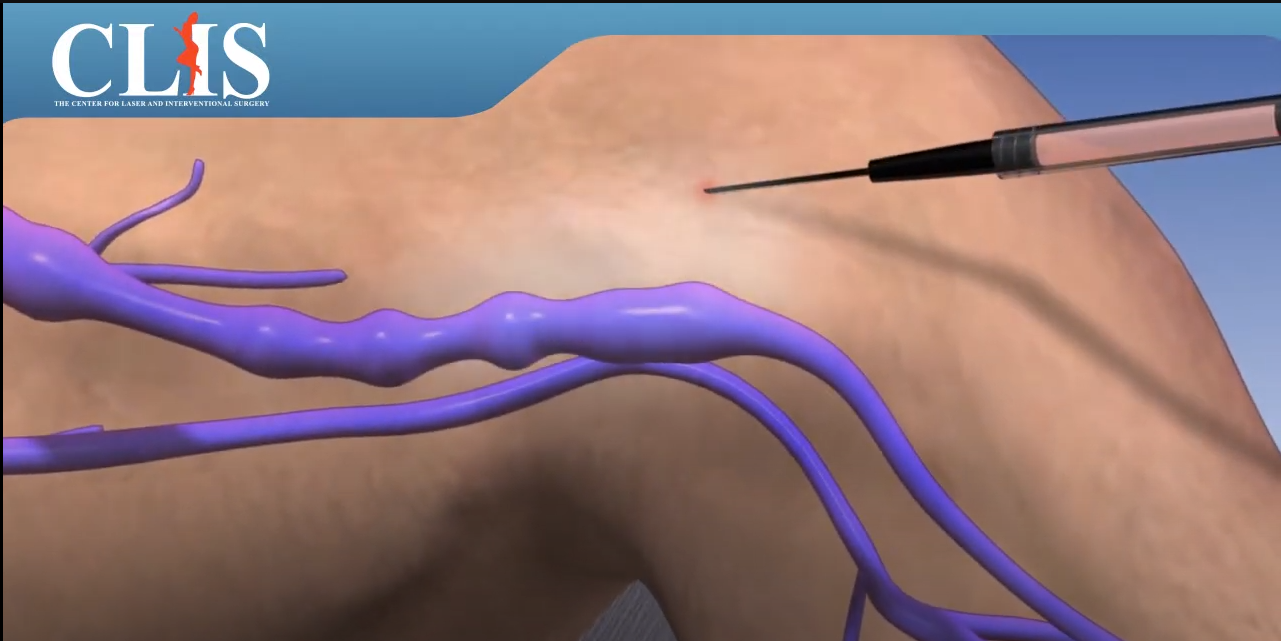
Varicose Veins

Varicose Veins
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a condition that occurs when the venous wall and/or valves in the leg veins are not working effectively, making it difficult for blood to return to the heart from the legs. CVI causes blood to “pool” or collect in these veins, and this pooling is called stasis.
Venous insufficiency and varicose veins symptoms include:
- Swelling in the lower legs and ankles, especially after extended periods of standing.
- Aching or tiredness in the legs.
- New varicose veins.
- Leathery-looking skin on the legs.
- Flaking or itching skin on the legs or feet.
- Stasis ulcers (or venous stasis ulcers).
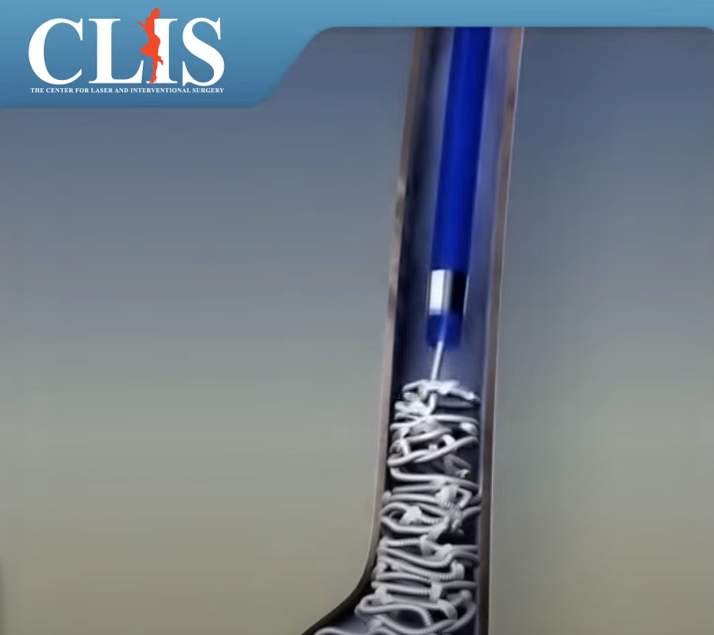
A minimally-invasive treatment is an outpatient procedure performed using imaging guidance. After applying local anesthetic to the vein, the interventional radiologist inserts a thin catheter, about the size of a strand of spaghetti, into the vein and guides it up the great saphenous vein in the thigh. Then laser or radiofrequency energy is applied to the inside of the vein. This heats the vein and seals the vein closed. Reflux within the great saphenous vein leads to pooling in the visible varicose veins below.
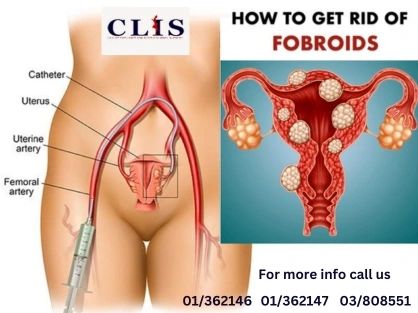
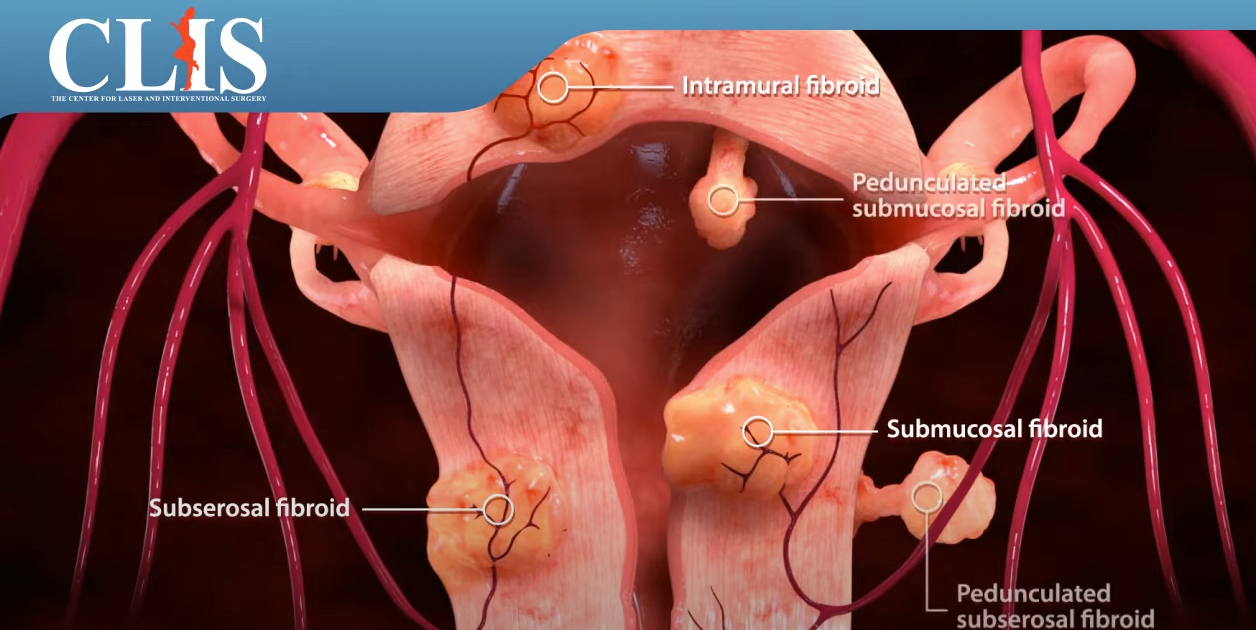
Uterine fibroid
pelvic artery embolization

Uterine fibroid
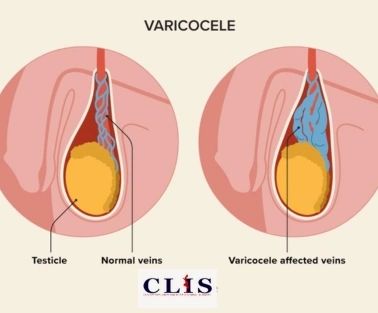
Testical vein embolization

Testical vein embolization
CLIS Center provides specialized care with minimally invasive embolization techniques to effectively manage varicoceles. This targeted treatment offers relief from discomfort and aims to enhance fertility prospects, all while avoiding more invasive surgical procedures.

prostate artery embolization

prostate artery embolization
Prostate health is vital to men’s overall well-being. As men age, their prostate expands, which can pose some significant health challenges like an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
50% of men between the ages of 51 and 60 are likely to develop this condition. However, an emerging minimally invasive technique called prostate artery embolization (PAE) is helping to address these symptoms so that men can get back to their day-to-day activities.
1-What is prostate artery embolization?
Prostate artery embolization is performed through a small puncture in the groin. A catheter is inserted through the artery and directed toward the prostate. Once the catheter is positioned in the artery supplying blood in the prostate, tiny particles are injected that plug up the artery, blocking blood flow.
2- Benefits of prostate artery embolization?
– It’s minimally invasive
– Lower risk of urinary incontinence
– Result can be experienced within a few days
– No sexual side effects
-.No need for a bladder catheter
– Less pain and discomfort during and after the procedure
Make An Appointment
Fill Our the below form and our team will contact you as soon as possible
Timing
Tuesday-Friday: 8:00 to 19:00
© Copyright 2025 by